Canada and the European Central Bank have initiated interest rate cuts, how much longer will the Federal Reserve take? With the global interest rate cut cycle underway, how will assets unfold?
The European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of Canada (BoC) have already embarked on an interest rate cut cycle.The European Central Bank has lowered its key interest rate to 3.75%, while the Bank of Canada has reduced its rate from 5% to 4.75%. These measures signal a shift towards looser monetary policies among major central banks worldwide.
- European Central Bank (ECB):
- Background and reasons: Due to the slowdown in the Eurozone’s economic growth and easing inflation pressures, policymakers hope to stimulate economic activity through moderate monetary easing and prevent the negative impact of overly tight monetary policy on the economy.
- Interest rate cut measures: Recently, the ECB lowered its key interest rate by 0.25 percentage points, from 4% to 3.75%. This marks the beginning of a new interest rate cut cycle aimed at addressing the weak economic growth and persistent inflation slowdown in the Eurozone.
- Background and reasons: Due to the slowdown in the Eurozone’s economic growth and easing inflation pressures, policymakers hope to stimulate economic activity through moderate monetary easing and prevent the negative impact of overly tight monetary policy on the economy.
- Bank of Canada (BoC):
- Interest rate cut measures: The Bank of Canada reduced its key interest rate from 5% to 4.75%. This also makes it one of the first major central banks globally to take action on interest rate cuts.
- Background and reasons: Canada’s economic growth has been weak, and inflation is gradually easing. Policymakers believe it is necessary to support the economy through interest rate cuts and prevent the real estate market from overheating again.
- Interest rate cut measures: The Bank of Canada reduced its key interest rate from 5% to 4.75%. This also makes it one of the first major central banks globally to take action on interest rate cuts.
- Federal Reserve (Fed):
- Expected actions: The Federal Reserve is expected to keep interest rates unchanged at the upcoming meeting, with the current federal funds rate at 5.5%, the highest level since 2001.
- Background and reasons: As the U.S. economy and job market gradually normalize, it is expected that the Federal Reserve will gradually follow the footsteps of other major central banks and begin the process of policy normalization. With further economic growth and inflation slowdown, the Fed may start cutting interest rates for the first time later this year, such as in September.
- Expected actions: The Federal Reserve is expected to keep interest rates unchanged at the upcoming meeting, with the current federal funds rate at 5.5%, the highest level since 2001.
The rate cuts by the European Central Bank and the Bank of Canada indicate that global monetary policy is entering a new phase. While there is currently no immediate urgency for the Federal Reserve to follow suit, it is expected to gradually begin policy normalization in the coming months. Investors should pay attention to policy changes by major central banks in order to adjust investment strategies and asset allocations.
Outlook of the Federal Reserve’s Policy
The Federal Reserve maintained its interest rates at its latest meeting, with the current federal funds rate at 5.5%. However, as the U.S. economy slows down and inflation pressures gradually ease, the market expects the Federal Reserve to potentially start cutting rates in the next few months. Here are some key factors and time expectations:
- Normalization of the economy and job market:
- Slowing economic growth: The U.S. economic growth has started to decelerate, with the impact of high interest rates becoming increasingly evident.
- Loosening job market: While the job market remains strong, signs of rising unemployment rates and slowing hiring activities indicate that the labor market is gradually normalizing.
- Slowing economic growth: The U.S. economic growth has started to decelerate, with the impact of high interest rates becoming increasingly evident.
- Easing inflation pressures:
- Slowing inflation: With stable energy and commodity prices, core inflation pressures are easing.
- Slowing wage growth: Labor market loosening helps slow down wage growth, which is crucial for reducing inflation.
- Slowing inflation: With stable energy and commodity prices, core inflation pressures are easing.
- Market expectations:
- Timing of rate cuts: According to market expectations, the Federal Reserve may start cutting rates for the first time in September 2024.
- Policy statement: The Federal Reserve has hinted at the possibility of one to two rate cuts in the future, depending on the performance of economic data and the continued trend of inflation.
- Timing of rate cuts: According to market expectations, the Federal Reserve may start cutting rates for the first time in September 2024.
The Impact of Global Interest Rate Cycles on Assets
The initiation of a global interest rate cutting cycle will have profound effects on different asset classes:
- Stock Market:
- Positive impact: Interest rate cuts generally benefit the stock market as lower rates reduce the financing costs for companies and increase investors’ risk appetite. Technology and growth stocks may perform well.
- Sector differences: Financial stocks may face pressure as the net interest margin for banks narrows due to the decrease in interest rates.
- Positive impact: Interest rate cuts generally benefit the stock market as lower rates reduce the financing costs for companies and increase investors’ risk appetite. Technology and growth stocks may perform well.
- Bond Market:
- Bond prices rise: Interest rate cuts help drive bond prices up, especially for long-term bonds, as yields and prices have an inverse relationship.
- Yield curve: Expectations for both short-term and long-term bond yields to decrease, investors may reallocate funds to long-term bonds to lock in higher yields.
- Bond prices rise: Interest rate cuts help drive bond prices up, especially for long-term bonds, as yields and prices have an inverse relationship.
- Commodity Market:
- Gold price rises: Interest rate cuts and loose monetary policies typically boost the price of gold as investors seek safe-haven assets.
- Oil and other commodities: Economic slowdown may negatively impact the demand for oil and other commodities, but the depreciation of the dollar due to interest rate cuts may partially offset this impact.
- Gold price rises: Interest rate cuts and loose monetary policies typically boost the price of gold as investors seek safe-haven assets.
- Real Estate Market:
- Lower financing costs: Interest rate cuts will lower mortgage rates, stimulating demand in the real estate market.
- Return on investment: A lower interest rate environment may drive real estate investments as properties with higher yields become more attractive.
- Lower financing costs: Interest rate cuts will lower mortgage rates, stimulating demand in the real estate market.
As the European Central Bank and the Bank of Canada take the lead in initiating interest rate cuts, the Federal Reserve is also expected to follow suit in the coming months. This global trend of interest rate cuts will have a broad impact on stock, bond, commodity, and real estate markets. Investors should closely monitor policy changes by major central banks and adjust investment strategies according to market dynamics.
As the European Central Bank and the Bank of Canada take the lead in initiating interest rate cuts, the Federal Reserve is also expected to follow suit in the coming months. This global trend of interest rate cuts will have a broad impact on stock, bond, commodity, and real estate markets. Investors should closely monitor policy changes by major central banks and adjust investment strategies according to market dynamics.

Historical Review: S&P Outperforming Industries and Risk Considerations during Rate-cutting Cycles
Outperforming S&P Industries
- Technology Industry
- Reasons: The technology industry typically benefits from rate cuts as lower interest rates reduce financing costs, promoting investment in research and innovation by companies. Additionally, investors tend to favor high-growth, high-risk tech stocks in a low-interest rate environment.
- Historical Performance: During the rate-cutting cycle following the 2008 financial crisis, technology stocks performed exceptionally well. For example, large tech companies like Apple and Microsoft saw significant stock price growth during this period.
- Reasons: The technology industry typically benefits from rate cuts as lower interest rates reduce financing costs, promoting investment in research and innovation by companies. Additionally, investors tend to favor high-growth, high-risk tech stocks in a low-interest rate environment.
- Consumer Discretionary Industry
- Reasons: Rate cuts typically stimulate consumer spending as borrowing costs decrease, giving consumers more disposable income to spend on non-essential items. This industry includes consumer goods such as automobiles, luxury goods, and electronics.
- Historical Performance: For instance, during the rate-cutting cycles of 2001 and 2008, stocks in the consumer discretionary industry showed strong performance.
- Reasons: Rate cuts typically stimulate consumer spending as borrowing costs decrease, giving consumers more disposable income to spend on non-essential items. This industry includes consumer goods such as automobiles, luxury goods, and electronics.
- Real Estate Industry
- Reasons: Rate cuts lower mortgage interest rates, stimulating demand in the real estate market and enhancing the profitability of real estate development and sales companies.
- Historical Performance: Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) generally perform well in a low-interest rate environment as investors seek stable income and capital appreciation.
- Reasons: Rate cuts lower mortgage interest rates, stimulating demand in the real estate market and enhancing the profitability of real estate development and sales companies.
- Financial Industry
- Reasons: While rate cuts may narrow banks’ net interest margins, they can indirectly enhance banks’ profitability by boosting loan demand and reducing bad debts. Insurance companies and asset management firms also benefit from increased market activity.
- Historical Performance: For example, the financial industry performed relatively well during rate-cutting cycles in the 1990s and early 21st century.
- Reasons: While rate cuts may narrow banks’ net interest margins, they can indirectly enhance banks’ profitability by boosting loan demand and reducing bad debts. Insurance companies and asset management firms also benefit from increased market activity.
Risk Warnings
- Inflation Risk
- Risk Description: Excessive interest rate cuts may lead to an increase in inflation. When interest rates are too low, consumption and investment activities increase, which may drive up price levels.
- Response Strategy: Investors should pay attention to the policy direction of central banks and inflation data, and adjust their investment portfolios promptly.
- Risk Description: Excessive interest rate cuts may lead to an increase in inflation. When interest rates are too low, consumption and investment activities increase, which may drive up price levels.
- Liquidity Risk
- Risk Description: In a low interest rate environment, a large amount of funds flowing into the stock market may lead to excess market liquidity. Once market confidence is shaken, it may trigger rapid fund outflows and market volatility.
- Response Strategy: Maintain appropriate cash reserves and liquidity management, and avoid excessive reliance on high-risk assets.
- Risk Description: In a low interest rate environment, a large amount of funds flowing into the stock market may lead to excess market liquidity. Once market confidence is shaken, it may trigger rapid fund outflows and market volatility.
- Interest Rate Reversal Risk
- Risk Description: If the economic conditions improve, central banks may quickly raise interest rates, which will impact industries that rely on a low interest rate environment.
- Response Strategy: Investors should closely monitor economic indicators and central bank policy statements, and prepare for interest rate hikes.
- Risk Description: If the economic conditions improve, central banks may quickly raise interest rates, which will impact industries that rely on a low interest rate environment.
- Credit Risk
- Risk Description: A low interest rate environment may lead to excessive borrowing by companies and individuals, increasing systemic risk. Once interest rates rise or the economy declines, it may result in a large number of defaults.
- Response Strategy: Pay attention to the financial health of companies and avoid investing in highly leveraged enterprises.
- Risk Description: A low interest rate environment may lead to excessive borrowing by companies and individuals, increasing systemic risk. Once interest rates rise or the economy declines, it may result in a large number of defaults.
💡 During a rate-cutting cycle, the technology, non-essential consumer goods, real estate, and financial industries typically perform well. However, investors should be mindful of inflation, liquidity, interest rate reversals, and credit risks, diversify their investments reasonably, and maintain the ability to adapt flexibly to market changes.
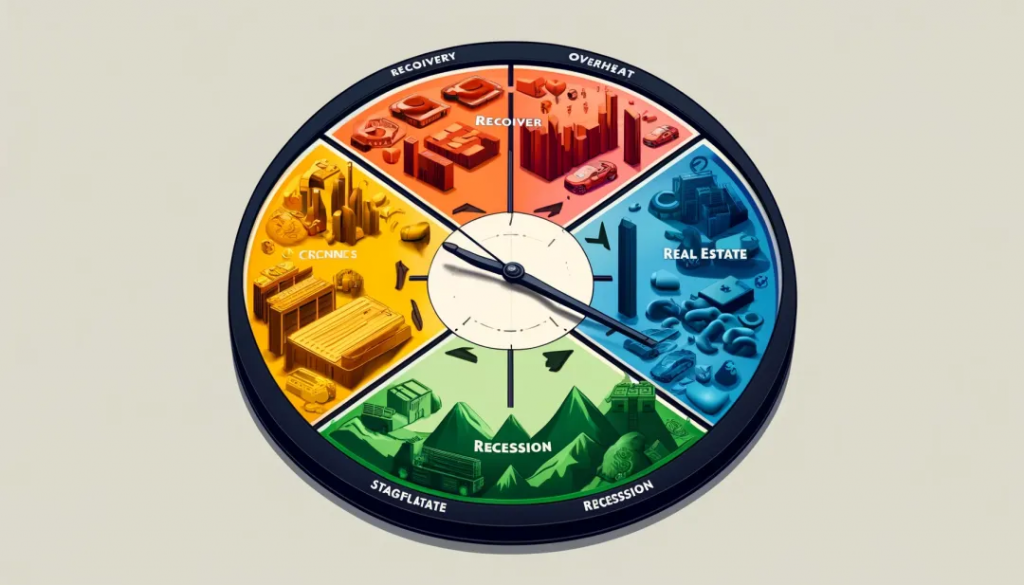
Analysis of Economic Trends and Asset Performance during Interest Rate Cut Cycles by Merrill Lynch Clock
- The Merrill Lynch Clock is a tool used to analyze the relationship between economic cycles and asset performance, dividing the economic cycle into four stages: recovery, overheating, stagflation, and recession. Each stage corresponds to different economic indicators and asset performance. The following is an analysis based on the Merrill Lynch Clock of the interest rate cut cycle:
- Recession
Characteristics:
- Slow or negative economic growth: GDP growth slows down, and corporate profits decrease.
- Low or decreasing inflation: Reduced demand leads to easing price pressures.
- High unemployment rate: Layoffs by companies lead to an increase in the unemployment rate.
- Central bank cuts interest rates: To stimulate the economy, central banks typically adopt an interest rate cut policy.
Corresponding asset performance:
- Bonds: Bond prices rise, especially long-term bonds, as the decrease in interest rates lowers bond yields (leading to price increases).
- Gold: As a safe-haven asset, the price of gold usually rises.
- Defensive stocks: Stocks from sectors such as utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare tend to perform relatively well.
- Recovery
Characteristics:
- Accelerated economic growth: GDP growth rate rebounds, and corporate profits improve.
- Low but gradually rising inflation: Demand recovers, prices gradually increase.
- Decreasing unemployment rate: Increased hiring by businesses leads to a decline in the unemployment rate.
- Continued low interest rates: The central bank maintains a low interest rate policy to support economic recovery.
Corresponding asset performance:
- Stocks: Especially cyclical stocks, such as technology stocks and non-essential consumer goods stocks, show strong performance.
- High-yield bonds: With economic recovery, credit risk decreases, leading to an increase in prices of high-yield bonds (junk bonds).
- Real estate: Low interest rate environment and economic recovery drive the real estate market up.
- Overheat
Characteristics:
- Rapid economic growth: GDP grows rapidly, and corporate profits reach their peak.
- High inflation: Strong demand causes prices to rise rapidly.
- Low unemployment rate: Labor market tightens, leading to wage increases.
- Central bank raises interest rates: To control inflation, the central bank starts raising interest rates.
Corresponding asset performance:
- Stocks: Cyclical stocks and growth stocks continue to perform well, but with increased volatility.
- Commodities: Prices of commodities such as crude oil and metals rise due to strong demand.
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS): Protect investors from the impact of inflation and perform relatively well.
- Stagflation
Characteristics:
- Economic growth slowdown: GDP growth slows down or stagnates, leading to a decrease in corporate profits.
- High inflation: Prices remain high.
High unemployment rate: Economic slowdown results in an increase in the unemployment rate.
- Central bank challenges: The central bank faces a dilemma between controlling inflation and promoting economic growth.
Corresponding asset performance:
- Gold: As a safe-haven asset, the price of gold usually rises.
- Defensive stocks: Stocks from industries such as utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare tend to perform relatively well.
- Cash and short-term bonds: Maintain liquidity to reduce the impact of market volatility.
💡 A specific analysis of the current interest rate cut cycle indicates that the economy is expected to transition from recession to recovery. Both the European and American economies are currently showing signs of a soft landing. The recessionary period may be very short-lived before entering a recovery phase. In the next stage, the marginal decrease in interest rates is likely to become a determining variable in market trends. Therefore, we recommend focusing on technology stocks and non-essential consumer goods.
The interest rate cut cycle in 2024
Currently (in 2024), the global economy is showing signs of slowing growth and weakening inflation. The European Central Bank and the Bank of Canada have already initiated interest rate cut cycles, with the Federal Reserve expected to follow suit in the coming months. Against this backdrop, the economy is in a phase of transition from stagnation to recovery:
- Bond Market: Bond prices, especially long-term bonds, are rising due to falling interest rates.
- Gold: As a safe-haven asset, gold performs well in times of increased economic uncertainty.
- Stock Market: Technology stocks and non-essential consumer goods stocks are performing strongly, supported by the low interest rate environment favoring high-growth industries.
- Real Estate: Low interest rates are driving an increase in demand in the real estate market.
Risk Considerations
- Risk of inflation rebound: Overly loose monetary policy may lead to a rebound in inflation.
- Risk of interest rate reversal: If the economy rapidly improves, central banks may raise interest rates again, dampening market confidence.
- Liquidity risk: An environment of interest rate cuts may lead to excess market liquidity and increased volatility.
End of text!
Leave a Reply