Disney — A Mediocre Company with “Magic”
Warren Buffett once said, “It’s far better to buy a wonderful company at a fair price than a fair company at a wonderful price.” Despite the fame of some companies, they are actually mediocre or even poor businesses.
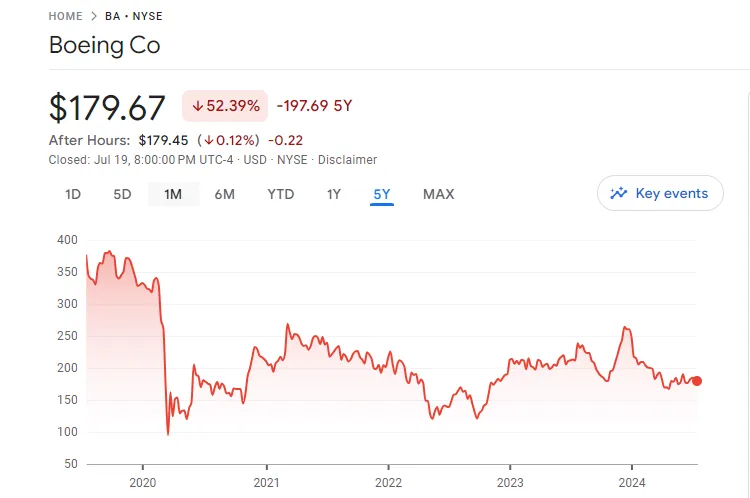
In our previous article “Boeing Plead Guilty and Accept Penalty! From a Giant to a ‘Junk Stock‘, How Can US Retail Investors Avoid the Minefield of Earnings Culture,” we detailed the process by which Boeing’s (BA) stock became a junk stock due to its earnings culture.
Today, we turn our attention to Disney (DIS), which, in my view, is a “dazzling” representative of mediocrity due to management issues. Although DIS is not as frequently the focus of stock reviews as the big tech sisters, it remains one of the hot topics in the market.
The Disney Company, this global entertainment giant shining with the glow of magic, began in 1923 and was co-founded by the dreamers, the Disney brothers.
For nearly a century, this company has grown into a diversified international family entertainment and media empire, capturing the hearts of audiences worldwide with its unparalleled creativity and spirit of innovation.
Disney possesses a strong moat:
- Exceptional brand influence: Disney has built a complete industry chain around IPs, including movies, television, theme parks, consumer products, etc., achieving all-around monetization of IPs. This industry chain integration capability is difficult for other competitors to imitate.
- A wealth of high-quality IP resources: Disney has accumulated a wealth of high-quality IP resources through independent innovation, historical resource mining, and mergers and acquisitions. These IPs include classic animated characters, Marvel superheroes, Star Wars, etc., providing the company with a continuous source of creativity and a stable source of income.
- A complete IP industry chain: The Disney brand has extremely high visibility and reputation worldwide, representing positive values such as joy and dreams, which has won the company a loyal customer base.
However, under these dazzling lights, it is hard to conceal Disney’s increasingly mediocre performance. First, the stock price has fallen by about 37% over the past five years, significantly underperforming the broader market.
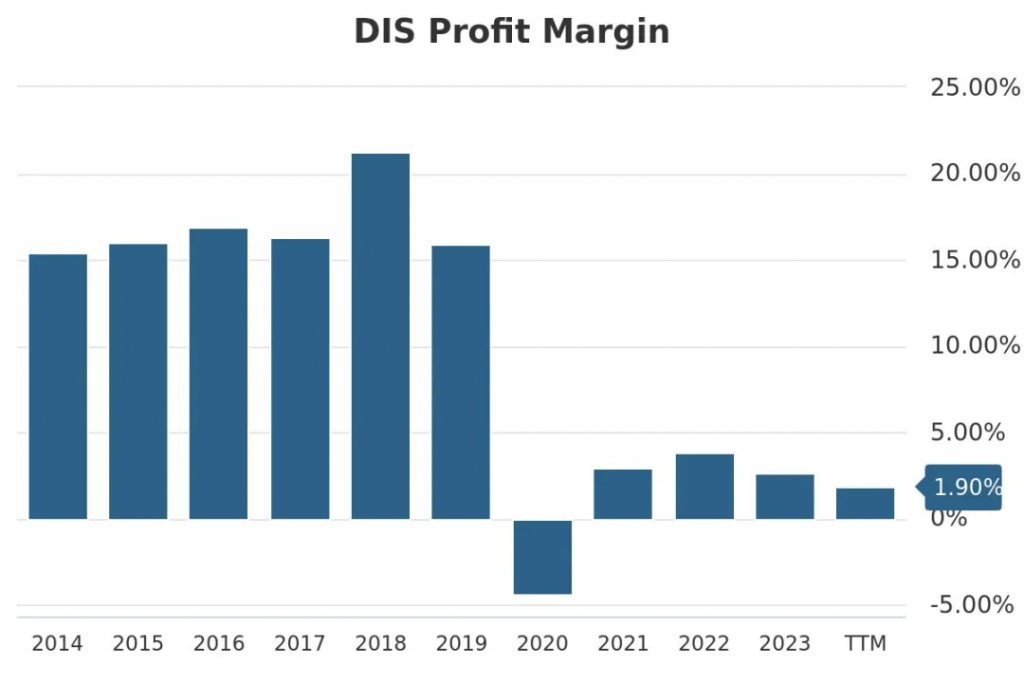
The low stock price trend is just a manifestation; the underlying cause is the weakening of its profitability. Looking at Disney’s net profit margin over the past decade, we find that since 2020, this company with strong competitive advantages has had a profit margin of less than 5%, with no trend of improvement.
Further analysis shows that Disney’s business is mainly divided into three segments:
- Entertainment business: In fiscal year 2023, revenue was $40.635 billion, with a profit of $1.444 billion, and a net profit margin of 3.55%.
- Sports business: In fiscal year 2023, revenue was $17.111 billion, with a profit of $2.465 billion, and a net profit margin of 14.41%.
- Experience business: In fiscal year 2023, revenue was $32.549 billion, with a profit of $8.954 billion, and a net profit margin of 27.51%.
It is clear that the experience business (including theme parks and cruises) is Disney’s most profitable segment, which aligns with the intuitive perception of ordinary consumers.
However, it is puzzling that Disney, with a wealth of high-quality IP resources, has suffered a significant setback in its entertainment business (including Disney+, Hulu, and ESPN+), with a profit margin far lower than its competitor Netflix’s 19.54%, which is quite disappointing.
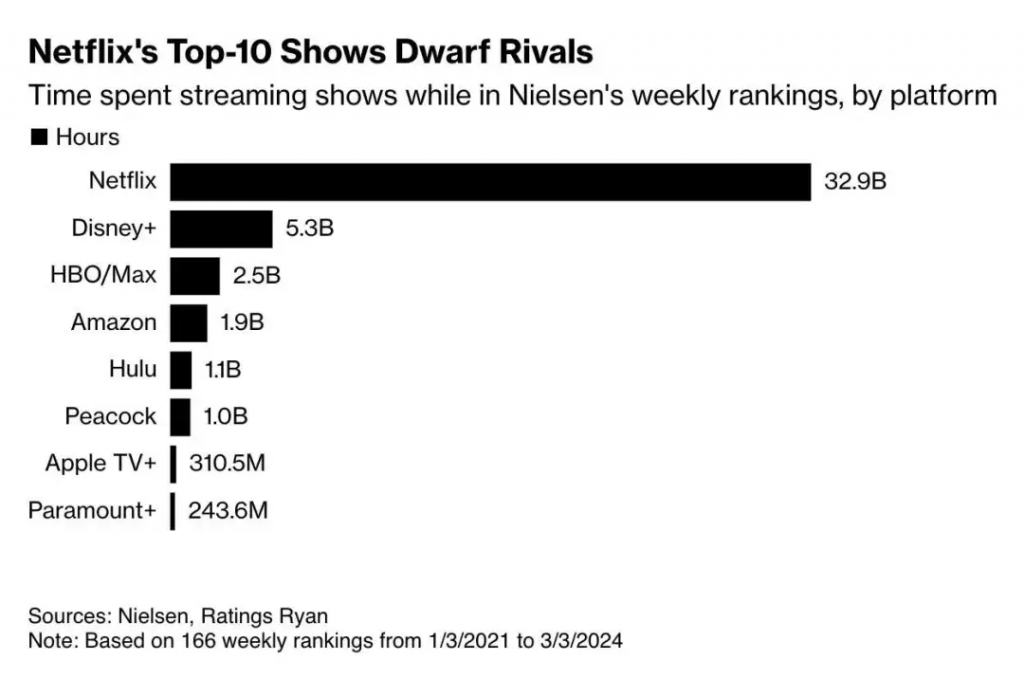
Disney officially entered the streaming business in 2019, and during 2020 to 2021, the number of Disney+ subscribers grew rapidly. Relying on Disney’s unparalleled brand influence and IP advantages, the market was full of expectations for its transformation into a streaming technology company.
As a result, many people began to worry that Netflix’s profitability would be challenged by Disney.
This phenomenon inevitably leads people to attribute the cause to management issues. A specific analysis of Disney’s profit margins shows that the overall gross margin is actually acceptable, maintaining above 30% over the past decade, such as 33.41% in 2023.
However, the operating profit margin for the same year was only 10.50%, which means that operating expenses such as management, sales, and advertising accounted for 68.72% of the gross margin.
In fact, Disney’s management has been criticized in recent years, affecting the company’s operational efficiency:
- Frequent leadership changes: Disney has experienced several ups and downs in leadership succession. In 2020, Bob Chapek succeeded as CEO, but due to his shortcomings in company strategy and communication, he was forced to step down after two years, and Bob Iger returned to the company as CEO. This frequent leadership change has led to internal instability and affected the continuity and execution of decision-making.
- Lack of succession planning: Disney has a noticeable deficiency in succession planning. After Iger returned as CEO in 2022, one of his top tasks was to find a suitable long-term successor. However, the lack of succession planning and uncertainty make the stability of the company’s future leadership a concern.
- Strategic and execution issues: Disney has invested heavily in the streaming business but faces high content production costs and fierce market competition. Although Disney+ has achieved some success in user growth, profitability remains a significant challenge. Disney has adopted a strategy in content production to reduce quantity and improve quality, especially in Marvel series movies. However, this strategy has not been significantly effective, and some movies and programs have suffered box office failures due to poor content quality and market feedback. In addition, the company has faced market resistance to some works due to their progressive themes when promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) content, affecting box office and revenue.
- Shareholder pressure and governance issues: Disney’s shareholders have questioned the performance of the company’s management, especially activist investor Nelson Peltz, who has criticized the company’s governance and strategy and is seeking a board seat to promote change. This shareholder pressure further exacerbates the instability of the management.
In summary, although Disney has a very strong moat, and analysts’ ratings for DIS stocks are mostly “buy” or “strong buy,” given the serious problems with the management, I do not recommend the stock. It is advised to wait and see until Disney solves its management issues and improves its net profit margin.